What do blood pressure readings mean? (blood pressure readings chart)
Blood pressure readings can change throughout the day depending on your circumstances. Factors such as stress, anxiety, food intake (caffeine and salt intake), smoking, and exercise can increase pressure.
The American Heart Association defines
- normal blood pressure as less than 120/80,
- elevated blood pressure ranges between 120/80 and 129/80, and
- high blood pressure is 130/80 and higher.
- In pregnancy, normal blood pressure should be below 120/80.
Blood pressure readings can change throughout the day depending on your circumstances. Factors such as stress, anxiety, food intake (caffeine and salt intake), smoking, and exercise can increase pressure.
The American Heart Association defines
- normal blood pressure as less than 120/80,
- elevated blood pressure ranges between 120/80 and 129/80, and
- high blood pressure is 130/80 and higher.
- In pregnancy, normal blood pressure should be below 120/80.
If you have other risk factors, such as diabetes or heart disease, your doctor may recommend medication in addition to lifestyle adjustments if your blood pressure is in the high range.
High blood pressure, such as 180/110 or greater, may be a sign of an emergency. Seek immediate medical attention if this high blood pressure is accompanied by chest pain, difficulty breathing, headache, lightheadedness, or back or stomach pain. If you get a high blood pressure reading like this but no accompanying symptoms, check it again in a short while, and if it’s still high, call your doctor or go to the emergency department.
Depending on the accompanying symptoms, you may have low blood pressure if your reading is less than roughly 100/60. Consult your doctor if you are unsure.
Blood pressure can be divided into five main sorts or categories. Systolic, diastolic, and necessary management are defined in the chart below.
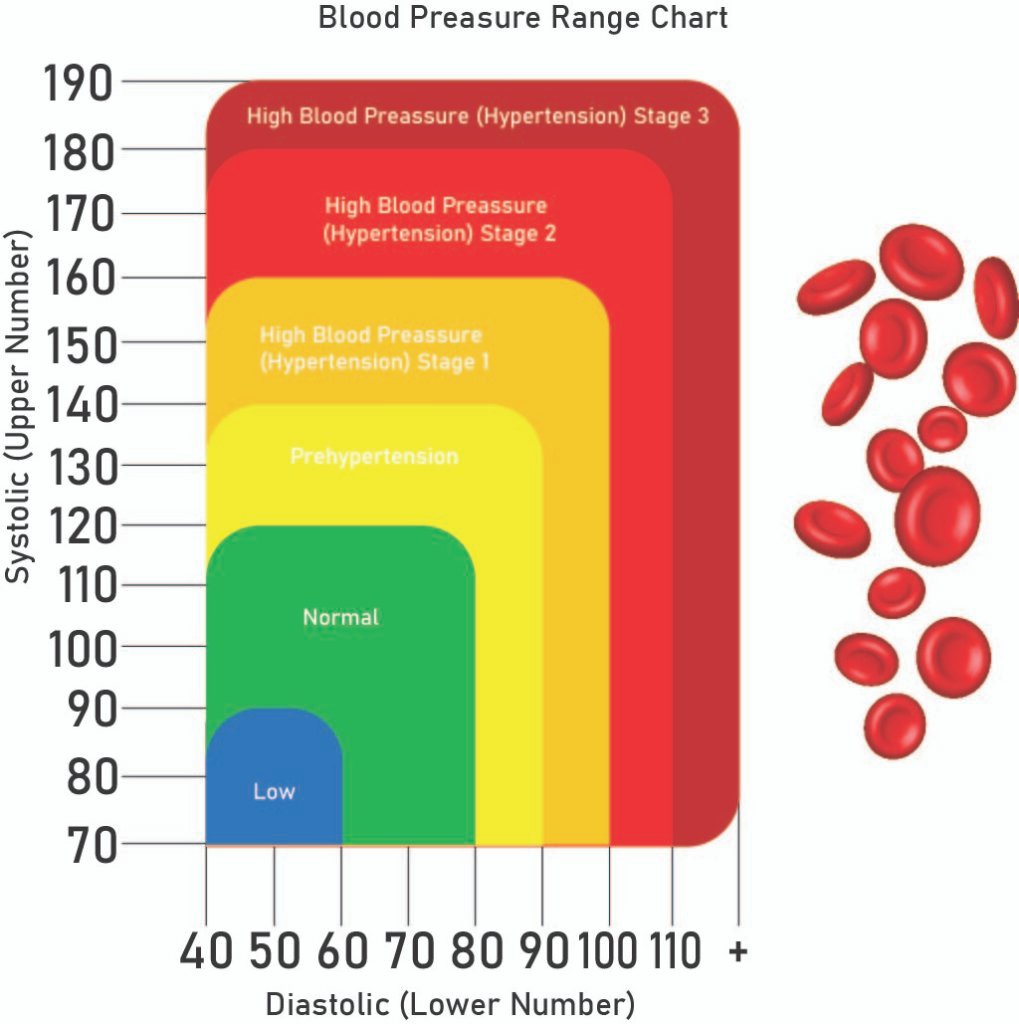
What is high blood pressure? What is normal blood pressure?
- Normal blood pressure is below 120/80.
- Blood pressure readings are given as two numbers:
- Systolic blood pressure (the highest figure) is equivalent to the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats.
- The pressure in the arteries as the heart relaxes is represented by diastolic pressure (the bottom number).
- Hypertension is a major public health problem. Using new guidelines for defining hypertension, the American Heart Association estimates that nearly half (46%) of adults in the United States have hypertension.
- Complications of hypertension include heart disease, kidney disease, arteriosclerosis (atherosclerosis or atherosclerosis), eye damage, and stroke (brain damage).
- High pressure (tension) in the arteries, which are the blood vessels that transport blood from the heart to the rest of the body, is what is referred to as high blood pressure (hypertension).
- In 2017, the American College of Cardiology released new guidelines for high blood pressure
- Blood pressure between 120/80 and 129/80 is elevated blood pressure, and blood pressure of 130/80 or above is considered high.
- The American Academy of Cardiology defines blood pressure ranges as:
- Hypertension stage 1 is 130-139 or 80-89 mm Hg, and hypertension stage 2 is 140 or higher, or 90 mm Hg or higher.
What are the signs and symptoms of high blood pressure?
Hypertension is asymptomatic, and hypertension is called the ‘silent killer’. Long-term high blood pressure can lead to a variety of complications, including heart attack, kidney disease, and stroke.
Some people have symptoms related to high blood pressure. These symptoms are:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Blurred vision
- The feeling of pulsations in the neck or head
- Nausea
What causes high blood pressure?
Hypertension is multifactorial, meaning that multiple factors combine to cause high blood pressure.
- High Salt Intake or Salt Sensitivity: This occurs in certain demographics, such as the elderly, African Americans, overweight people, and those with kidney problems.
- Genetic Predisposition to Hypertension: People with one or two hypertensive parents have about twice the incidence of hypertension as the general population.
- Certain arterial abnormalities leading to increased resistance (stiffness or lack of elasticity) of small arterioles (arterioles): This increased stiffness of peripheral arterioles is associated with obese people, sedentary people, and salt intake. occurs in many people. old.
What alternative therapies help lower and manage high blood pressure?
Several complementary and alternative medicine strategies can help control high blood pressure and prevent it from rising further.
- Reduce stress.
- Use relaxation methods such as deep breathing, imagery relaxation, yoga, meditation, and biofeedback.
- Keep a daily blood pressure chart.
- Get adequate sleep.
- Some home remedies such as garlic, coenzyme Q-10 (CoQ10), calcium, magnesium, fish oil, and flaxseed have been shown to lower blood pressure. please give me.

